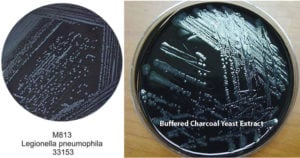
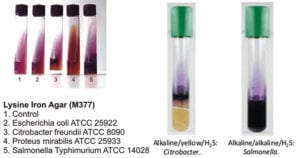
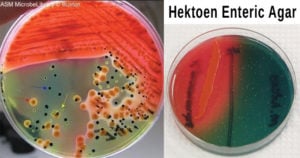
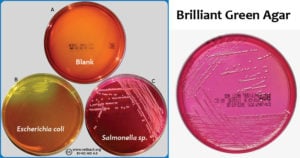
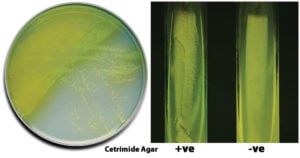
BCYE Agar- Composition, Principle, Preparation, Results, Uses
Feeley et al in 1978 developed a medium to isolate Legionella species which was later modified by substituting yeast extract for casein hydrolysate and beef extract, and replacing starch with activated … Read more