- The preimplantation period of human embryo development is remarkable and characterized by successive changes in terms of genetic control, physiology, and morphology of the embryo.
- Blastocyst (Greek, blastos= sprout + cystos = cavity) is a distinctive stage of mammalian embryo development, characterized by a hollow cellular mass that forms in early development.
- It is an embryo that has developed for five to six days after fertilization.
- It is a form of blastula developing from a berrylike cluster of cells called the morula.
- When a cavity appears in the morula between the cells of the inner cell mass and the enveloping layer, it is called as the
- Blastocoel is a cavity filled with fluid containing high concentrations of lactate and specific amino acids and lower concentrations of glucose and pyruvate.
- The blastocyst differs from the blastula in that it is composed of two already differentiated cell types, the inner cell mass and the enveloping layer, trophoblast.
- The inner mass of cells are destined to become the embryo proper and an outer rim of cells called the trophoblast.
- It is the trophoblast that forms the attachment to maternal decidual tissue and gives rise to the fetal membranes and the definitive placenta.
- Cells of the trophoblast proliferate and form the multinucleated syncytiotrophoblast whose specialized functions enable it to destroy adjacent decidual cells and allow the blastocyst to penetrate deep into the uterine endometrium.
- The blastocyst floats freely in the uterine cavity for about a day before it implants, normally on about the fifth day after ovulation.
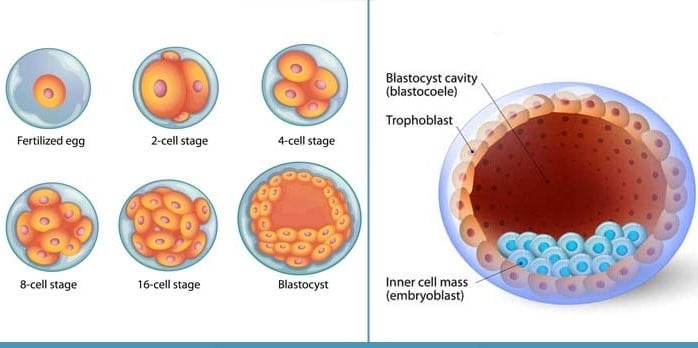
Image Source: garbhagnan.com
Interesting Science Videos
Stages of Blastocyst Embryo Development
The stages of blastocyst embryo development are divided into four grades.
Grade 1: The embryo with a blastocoel cavity less than 50% of the embryo volume.
Grade 2: The embryo with a blastocoel cavity as much as 50% of the embryo volume or more.
Grade 3: Embryo that has a blastocoel cavity which has fulfilled that all embryos and zona pellucida (ZP) appeared to be thinner than embryo on day 3.
Grade 4: Embryo that has successfully hatched from ZP.
Significance of Blastocyst
In normal conditions, after fertilization, the embryo grows until the blastocyst stage. The blastocyst grows as the cells divide and the cavity expands, where it “hatches” from the zona pellucida to implant into the endometrium.
- The blastocyst is the highest degree of development that an embryo can reach in vitro.
- At the blastocyst stage, the trophectoderm of the developing embryo acquires competency to attach to the receptive uterine luminal epithelium that has been appropriately primed with the steroid hormones estrogen and P4 ie. blastocyst is the stage when implantation occurs.
- An implantation-initiating adhesion cascade begins upon the engagement of cell adhesion molecules at the luminal epithelial and trophectoderm surface of the blastocyst. Many of these adhesion molecules transduce the signals necessary to sustain embryonic and maternal contributions to the formation of a placenta that supports fetal development through the term.
- In in vitro fertilization (IVF), the blastocyst culture is important to increase the success rate of IVF because of better embryo selection after better genomic activation and endometrial receptivity.
References
- Gilbert, S. F. (2000). Developmental biology. Sunderland, Mass: Sinauer Associates.
- Schoenwolf, G.C., Bleyl, S.B., Brauer, P.R., Francis-West, P.H. & Philippa H. (2015). Larsen’s human embryology (5th ed.). New York; Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone.
- Sadler, T. W., & Langman, J. (2004). Langman’s medical embryology. Philadelphia, Pa: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
- Moore, K. L., Persaud, T. V. N., & Torchia, M. G. (2008). The developing human: Clinically oriented embryology. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders/Elsevier.
- http://www.biologydiscussion.com/human-development/notes-on-blastocyst-implantation-of-blastocyst/5141
- https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Blastocyst_Development
- https://www.britannica.com/science/blastocyst
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/neuroscience/blastocyst
- https://www.intechopen.com/books/embryology-theory-and-practice/human-blastocyst-formation-and-development
