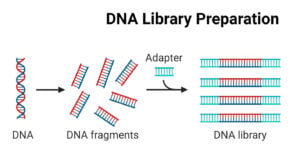
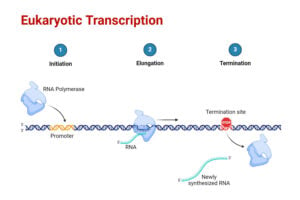
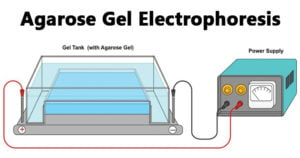
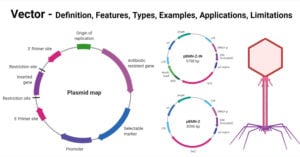
Sanger Sequencing: Principle, Steps, Applications, Diagram
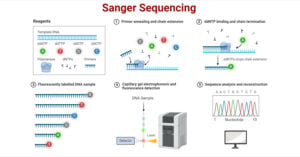
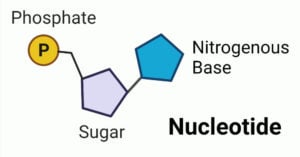
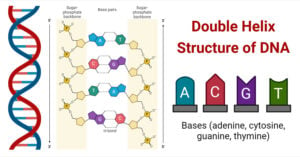
Sanger sequencing is a method that identifies the order of nucleotide bases in DNA based on chain termination by modified nucleotides called dideoxynucleotide triphosphates (ddNTPs). It is also known as … Read more