What is Calcofluor White Staining?
- Calcofluor white is a chemifluorescent blue dye that is nonspecifically used to bind to the beta linked-polysaccharide polymers of amoebic cysts.
- It functions by being able to bind to 1-3 beta and 1-4 beta polysaccharides on chitin and cellulose that is present in cell walls on fungi, plants, and algae.
- Due to the speed in examining the cells, the stain was replaced by Potassium Hydroxide (KOH) wet mount, which is quicker.
Interesting Science Videos
Objectives
- To stain fungal and parasitic elements
- To observe the presence of fungal and parasitic elements under a fluorescent microscope
Principle of Calcofluor White Staining
- Calcofluor white staining technique was used as a comparative stain specifically for the identification of Onychomycosis fungal infection.
- The chitin containing structures that fluoresce bright white under ultraviolet light in a fluorescent microscope.
- Calcofluor White stain as a non-specific fluorochrome that binds to chitin and cellulose cell walls, has been described to be the most rapid technique for detection of pathogenic fungi and yeasts such as Pneumocystis carinii, Microsporidium, Acanthamoeba, Naegleria, and Balamuthia species.
- Calcofluor White Stain visualizes well when mixed with potassium hydroxide for fungal elements.
- The counterstain used is Evans Stain which forms a dark background that enables the tissues and cells to fluoresce using blue light excitation and not UV rays.
- Other elements fluoresce reddish-orange while fungal and parasitic elements fluoresce bright apple-green.
Reagents
- Calcofluor white stain
- Potassium Hydroxide
Procedure of Calcofluor White Staining
- Carefully put the specimen on a clean glass slide
- Add a drop of Calcofluor White Stain to produce an intense fluorescence
- Add one drop of 10% Potassium Hydroxide
- Cover the specimen with a coverslip and leave it to absorb the stain for 1 minute
- Remove excess dye with a dry paper towel by gently pressing on the stain
- Observe the stain under ultraViolet rays at x100-x400 magnification.
Results
Fungi, Pneumocystis cysts, and parasites appear brilliant apple-green under UV fluorescent microscope, Violet and Blue light.
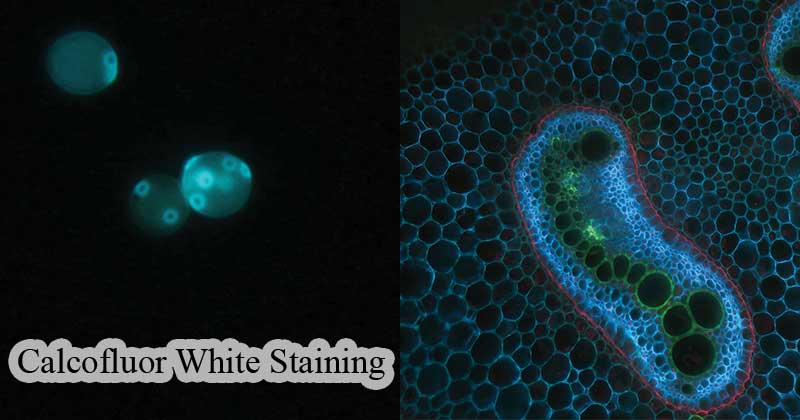
Figure: a: The fluorescent staining of yeast with calcofluor-white. The yeast shows a vivid blue color for the cell walls.
b: The cross-section of an Eagle Fern shows the bright green and bright blue fluorescence seen with CFW. Source: Calcofluor-white
Interpretation
Calcofluor white aqueous solutions absorb fluorescence over the range of 300 to 412-nm, with an absorbance peak
at 347-nm. The maximum excitation and fluorescence occur with ultraviolet light, although excitation with violet or blue-violet light also gives good results. Tissues show a yellowish-green background fluorescence with fungi and parasites showing more intense and more visible.
Applications of Calcofluor White Staining
- Calcofluor White stain can be used in Clinical Mycology and Parasitology:
- to demonstrate the presence of amoebic parasites by identifying their cysts.
- stain bud scars of yeast cells with a higher content of chitin enabling quantification of the bud scars which indicates the age of the cell.
- CFW is also used to strengthen the response of yeats in a pap smear in Papanicolaou stain.
- Used to stain Pneumocystis, microsporidia, Cryptosporidium, and some parasitic cysts which are calcofluor positive
- Detection of Candida in cancerous and precancerous lesions using CFW under fluorescent microscopy
- Calcofluor is also used as a dye in white-colored clothing, forming a black lighting appearance.
- CFW is a fabric brightening dye which is water-soluble and colorless. Hence its added to detergents as a cloth whitener
Advantages
- It is a quick and easy way to diagnosis in cytopathology and histopathology
- It doesn’t need any special reagents to make the stain effective.
Limitations
- It is expensive
- It may not be accurate on some occasions
Video of Calcofluor staining of Rotifer trophi
References
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/agricultural-and-biological-sciences/calcofluor-white
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Calcofluor-white
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/mucicarmine-stain
- http://biology.fullerton.edu/facilities/em/Library/calcofluor.pdf
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK288/
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/277230586_Calcofluor_White_A_Review_of_its_Uses_and_Applications_in_Clinical_Mycology_and_Parasitology
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/calcofluor-white
