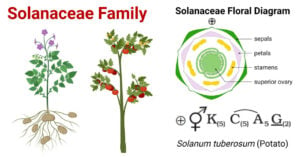
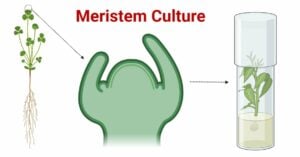
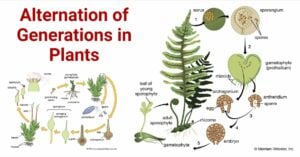
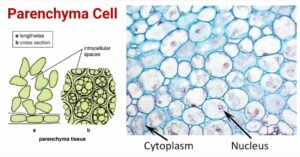
Solanaceae Family (Night Shade or Potato Family)
Systematic Position of Solanaceae Family Kingdom Plantae (Plants) Subkingdom Tracheobionta (Vascular plants) Superdivision Spermatophyta (Seed plants) Division Magnoliophyta (Flowering plants) Class Magnoliopsida (Dicotyledons) Subclass Asteridae Order Solanales Family Solanaceae Distribution of Solanaceae Family Habit and … Read more