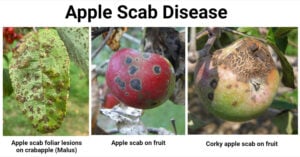
Apple Scab Disease: Causes, Symptoms, Cycle, Epidemiology
Apple Scab Disease is one of the most destructive diseases that affects the yield, fruit quality, and overall economic viability of apples and crab apples. It was first distinguished during … Read more